LEVER ACTUATED MAGNETIC CHUCKS
The magnetic chuck with permanent magnet are special equipments that guarantee to fix the metal pieces to facilitate the milling and grinding processing with machine tools. The pieces are fixed by rotating a lever, considerably reducing the set-up times of the parts on the machine bed. Different polarities are used depending on the size of the piece and the type of mechanical processing to be performed.
COMPLETE RANGE
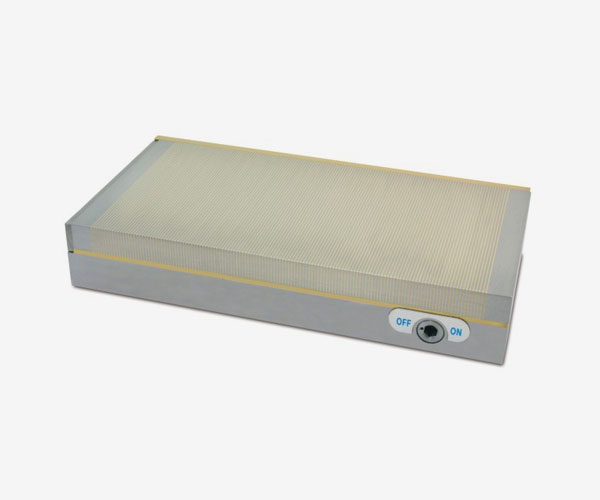

PMNM
Polar pitch 1.4-0.5 mm., Holding force 100N / Cm2, for grinding or light milling.
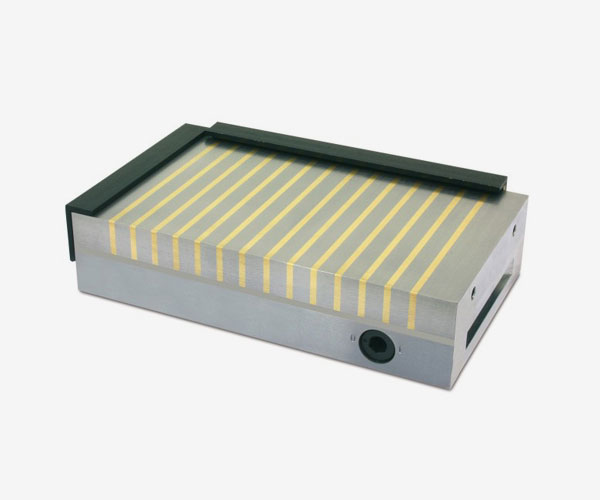

PMNEO
Polar pitch 11-4 mm., Holding force 150N / Cm2, for heavy milling operations.
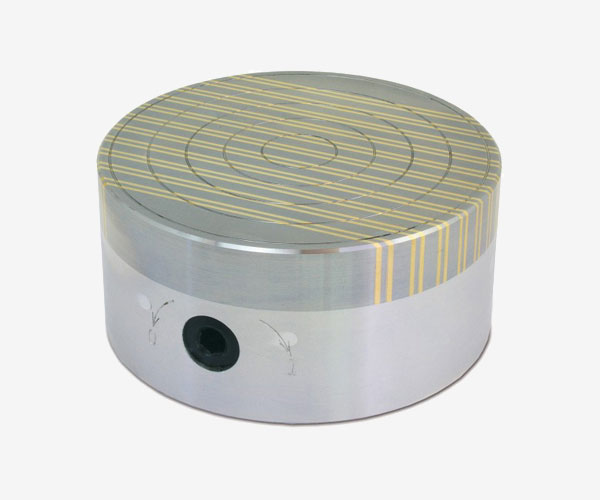
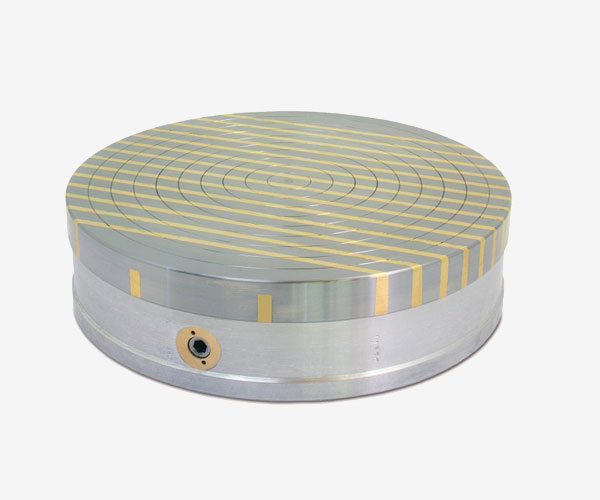

RF
Polar pitch 4 / 6-2 mm., Holding force 80N / Cm2, for turning and grinding operations.
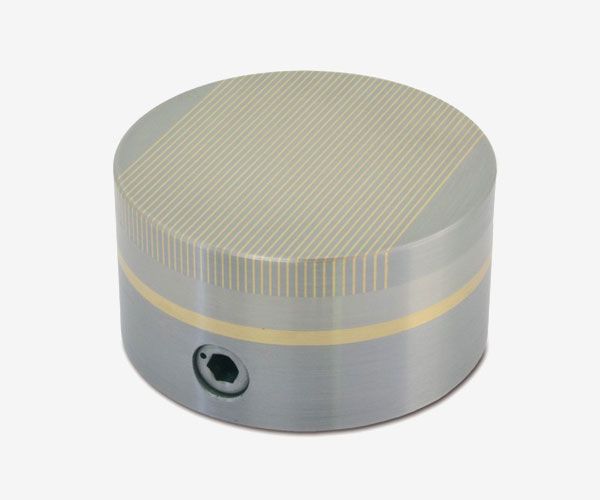

RNF
Polar pitch 1.5 / 0.5 mm., Holding force 80N / Cm2, for turning and grinding of small parts with thin thicknesses.
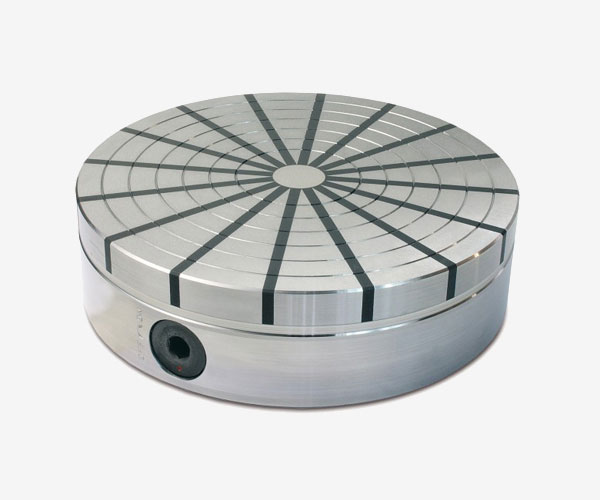

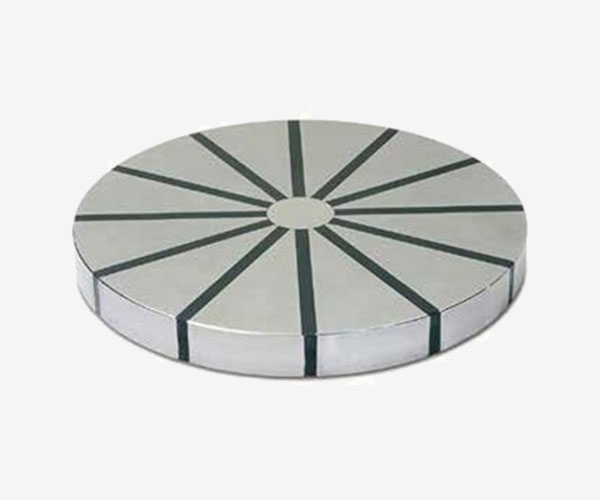
RS
Polar radial pitch, holding force 140N / Cm2, for turning and milling of rings and fifth wheels even at high speeds.
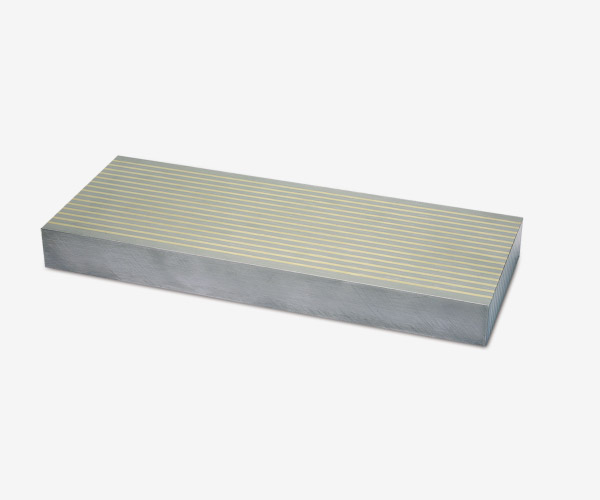

BL1 e BL2
Over lamellar plates to be used together with the magnetic planes if, due to the reduced thickness, shape or poor magnetic properties of the material, the magnetic anchoring operations are difficult.

FAQs
INFORMATIONS
