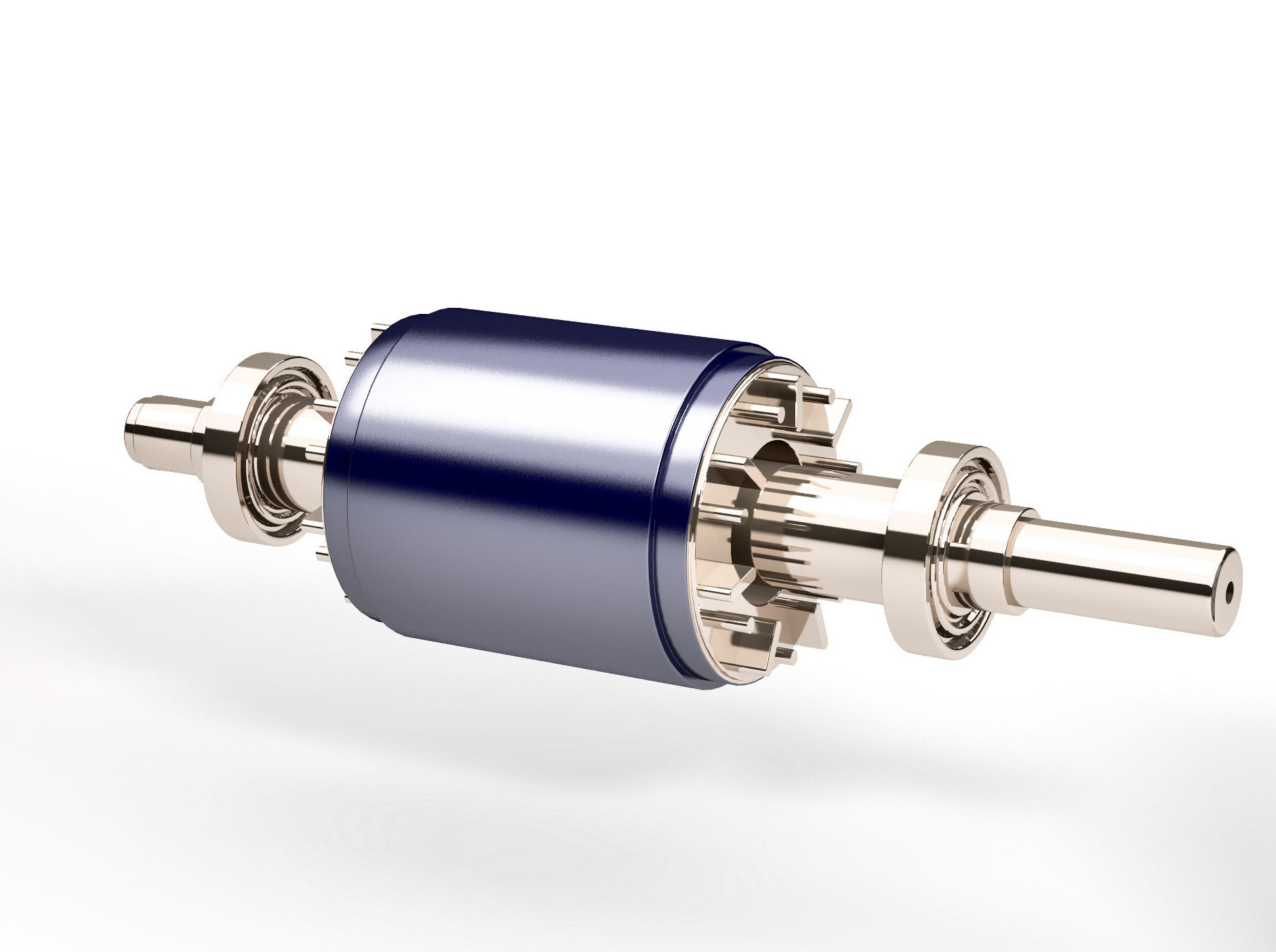
NEODYM
It represents the most modern family of permanent magnets and is made up of an alloy of Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB). Neodymium magnets are the most powerful permanent magnets on the market, with the maximum energy product, from 210 kJ / m3 to 420 kJ / m3. They are magnets with a formidable combination of high remanence and great coercive force. The uses can be all those in which excellent magnetic properties with small component size are required.
The powders of Nd-Fe-B are aligned through an oriented magnetic field and pressed into a mold, subsequently the sintering process takes place in an inert environment. The obtained Neodymium block is then mechanically worked to obtain the desired dimensions and shapes. These magnets have great potential to improve the performance of many applications considering their low cost. For this reason they will have the greatest impact on the development of permanent magnet devices in the near future.
COMPACT DESIGN
Neodymium magnets have the best magnetic flux properties in very small dimensions. They can be supplied in many forms.
HIGH PERFORMANCES
They have the highest energy density available on the market. For this reason they are used in many applications, they offer the best magnetic performance for same size.
EASY TO PROCESS
They are among the easiest magnets to cut and drill; they can be shaped in complex and irregular forms to suit special applications.
RESISTENCE
These magnets have a high coercive force, therefore a remarkable resistance to demagnetization.