ELECTROMAGNETS
These magnetic solenoids consist of an electromagnetic system without locking. The open magnetic circuit (under voltage) allows to hold or block ferromagnetic pieces.
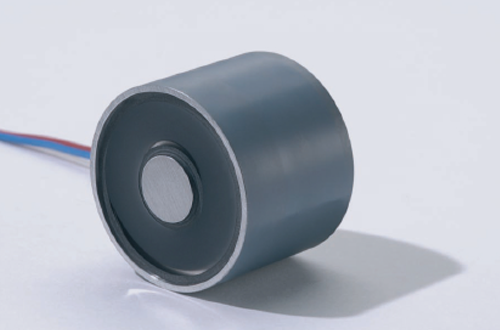
Circular Electromagnets
24V circular electromagnets with sealed encapsulated coil IP 54, nickel-plated outer body, power supply cable in the rear. On request they are also available with side cable exit.
COMPLETE RANGE

Circular Electromagnets
B Series

Circular Electromagnets
H Series

Block Shape
Electromagnets

Thin
Electromagnets

Electropermanent magnets
Block Shape
Circular Electropermanent
Magnets
FAQs
TECHNICAL AND OPERATING
INFORMATIONS
INFORMATIONS
